SQLTrace¶
Overview¶
SQLTrace is a Windows service that was initially created to monitor a Microsoft SQL Server instance with main focus on the performances of queries.
Microsoft SQL Server by itself exposes a variety of Windows Performance Counters metrics that can be collected with telegraf agent.
SQLTrace also extends and integrates into Neteye’s ITOA module gathering and processing additional data. As a strong point it provides metrics with a context, which helps in the analyzes: sqlinstance, sqluser, sqlsession, clienthost and more.
Over time a number of additional modules have been introduced to extend the monitored areas of SQL Server:
transactions
locks
headblockers
deadlocks
database growth
Another class of modules has been introduced to cover monitoring of external applications using SQL Server as database, which at the moment are:
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations
Usage Scenarios¶
Identify resource consuming queries¶
Workload generates a huge amount of queries and it is not immediate to identify those that are consuming the most resources. With SQLTrace it is really straightforward to identify the cost of queries in a given time interval through all the necessary metrics: cpu time, elapsed time, writes, reads, number of executions.
Identify bad query execution plans¶
The same query can have very different performances under different conditions: this is typically due to the execution plan. SQLTrace allows you to check which execution plan is in use in a certain time interval, and then to view it in SQL Server Management Studio.
A famous and annoying problem like bad parameter sniffing execution plan is easly detected and solved with SQLTrace.
A/B testing¶
SQL Server developer & admins introduce changes such as for example creating an index: SQLTrace immediately measures the impact of this change on queries duration and resource consumption.
Identify and solve long running transactions¶
SQL Server admins have to take into account long running transactions, which damage both the optimal functioning of the SQL Server instance and the application workflow (e.g. an ERP) on top of SQL Server. SQLTrace helps solving the problem and understand the root causes for a definitive solution.
Headblockers¶
Who deals with SQL Server knows that it bases on locks. A very bad situation can occur when for a wide variety of possible reasons in this hell of locks one or more transactions block other transactions. SQLTrace aids in quickly and confidently identifying the headblocker allowing to reactivate the workflow and analyze the source of the problem.
Monitoring of Microsoft SQL Server Queries’ Execution¶
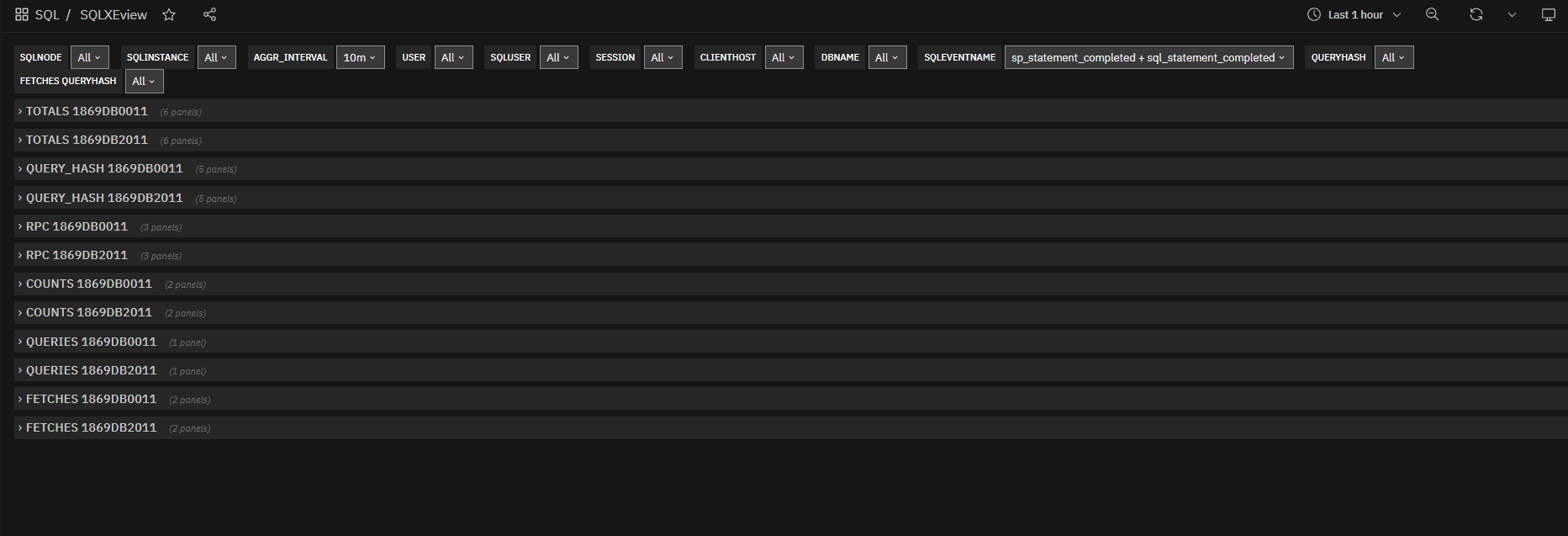
Fig. 179 SQLXEview dashboard¶
Exposed metric: sqlXeEvents¶
sqlXeEvents metric collects details on queries execution and it is based on Extended events of type sp_statement_completed,sql_statement_completed,rpc_completed.
sqlXeEvents,SqlQueryHash=2227549628205840796,SqlEventName=sp_statement_completed,SqlHostName=axpraos01,AxUser=axuser1,SqlUser=dm\aossvcuser,DatabaseName=axproddb,result=OK,host=axprodsqlnode,SQLInstance=axprodsqlnode,uniquifier=0 isFetch=0i,queryplan_hash=2227549628205840796,hex_queryplan_hash=0x1EE9D895B4C3399C,hex_query_hash=0x1EE9D895B4C3399C,cpu_time=32132i,duration=37132i,logical_reads=19i,physical_reads=0i,row_count=0i,writes=0i,session_id="73",session_id="8125"
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
SqlQueryHash |
queryhash in decimal format |
SqlEventName |
Extended event type, possible values:sp_statement_completed,sql_statement_completed,rpc_completed |
SqlHostName |
Host that produced the query |
AxUser |
AX user_id |
SqlUser |
SQL user_id: it is a domain user |
DatabaseName |
Database name |
result |
For rpc_completed events only, possible values: OK,Error,Abort |
host |
Hostname of server hosting SQL Server instance |
SQLInstance |
SQL Server instance |
uniquifier |
Technical tag inserted to avoid data-loss |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
isFetch |
Boolean, value 1 if query is a fetch |
queryplan_hash |
String, queryplan_hash in decimal format |
hex_queryplan_hash |
String, queryplan_hash in hexadecimal format |
hex_query_hash |
String, queryhash in hexadecimal format |
cpu_time |
Integer, microseconds of cpu time |
duration |
Integer, microseconds of elapsed time |
logical_reads |
Integer, number of pages read from buffer |
physical_reads |
Integer, number of pages read from storage |
row_count |
Integer, number of rows affected |
writes, number of pages written |
Integer, number of pages written |
session_id |
String, SQL session_id (spid) |
AxSession |
String, AX session_id |
Totals¶
sqlXeEvents metric with detail of event type: gives an efficient view on query execution engine status.
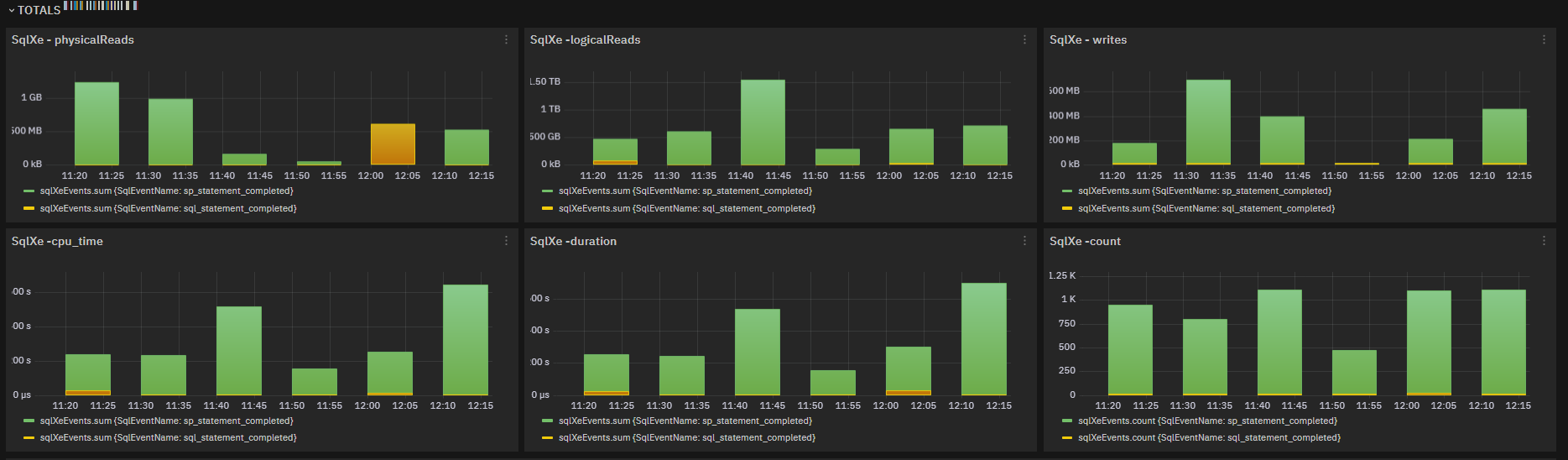
Fig. 180 sqlXeEvents charts for physical_reads,logical_reads,writes,cpu_time,duration,count grouped by SqlEventName¶
Query hash statistics¶
sqlXeEvents is a metric with detail of queryhash and gives an efficient view on how each query is performing.

Fig. 181 sqlXeEvents charts for cpu_time,duration,physical_reads,logical_reads,writes grouped by SqlQueryHash¶
RPC events¶
sqlXeEvents is metric limited to event type rpc_completed and it is immediate to see if there are queries ending in an error or killed (by an admin, system itself ..).
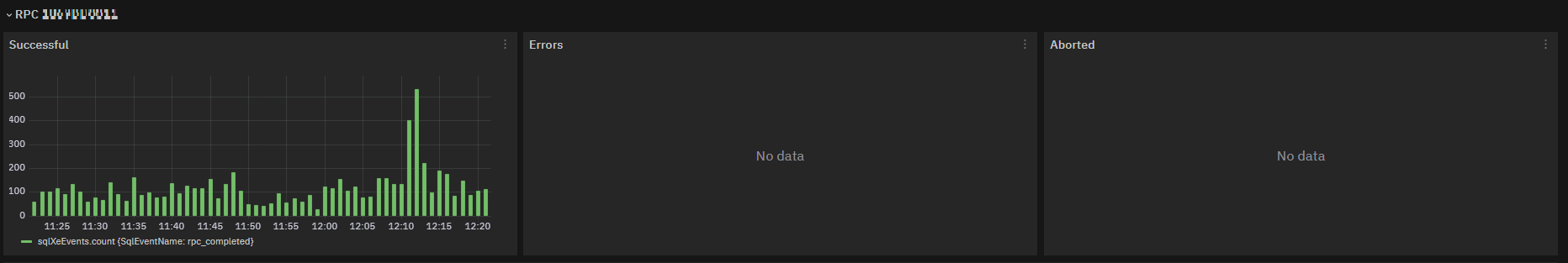
Fig. 182 sqlXeEvents result field charts with SqlEventName equal to rpc_completed¶
Query hash/users count¶
sqlXeEvents is a metric with detail of queryhash and AX user and it is straightforward way to see which user is calling an interesting query.
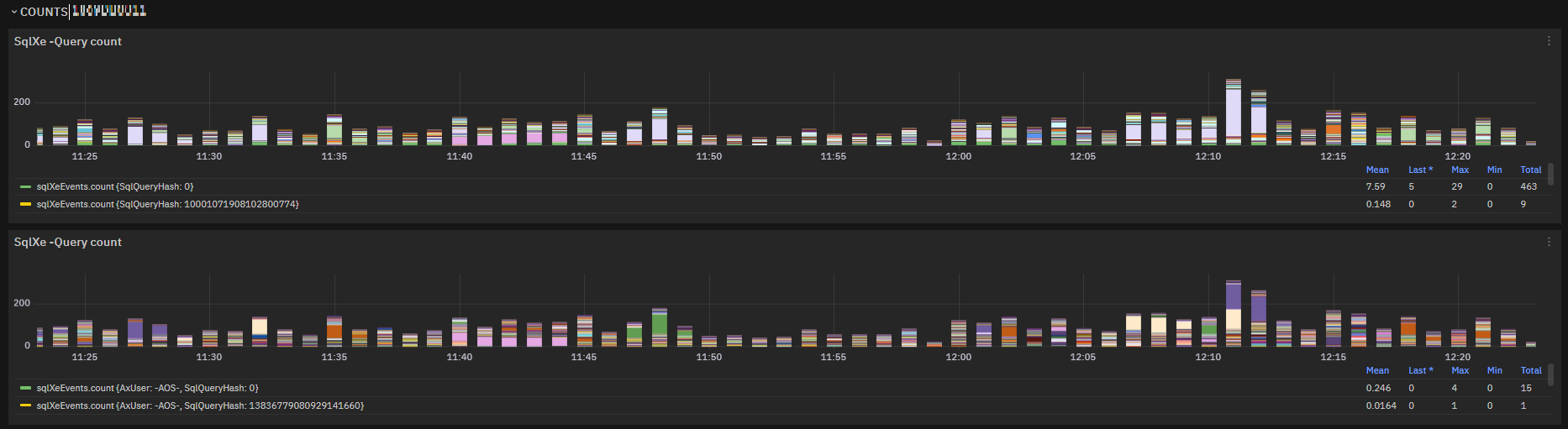
Fig. 183 sqlXeEvents charts for count grouped by SqlQueryHash and AxUser¶
Detail table¶
sqlXeEvents metric exposed in a table where we can search and visualize each single event.
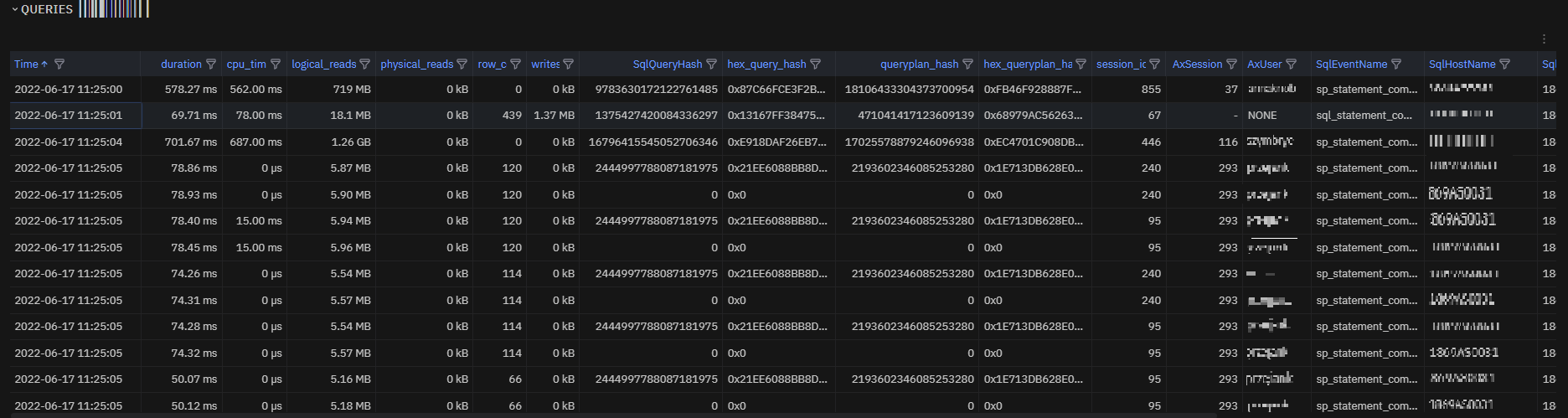
Fig. 184 sqlXeEvents table¶
Exposed metric: sqlXeFetches¶
sqlXeFetches is a metric that collects details on fetches built with a structure very similar to sqlXeEvents to make links easier. It is based on Extended events combined with queries on DMVs.
The great benefit of this metric is the possibility to know the query linked to fetches, which is natively not possible in SQL server.
sqlXeFetches,uniquifier=0,SQLInstance=axprodsqlnode,host=axprodsqlnode,query_hash=2227549628205840796,query_plan_hash=2227549628205840796,query_plan_hash_hex=0x1EE9D895B4C3399C,query_plan_hash_hex=0x1EE9D895B4C3399C,SqlHostName=axpraos01,AxUser=axuser1,SqlUser=dm\aossvcuser cpu_time=32132i,duration=37132i,logical_reads=19i,physical_reads=0i,row_count=0i,writes=0i,session_id="73",cursor_id="180261859",AxSession="8125"
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
uniquifier |
Technical tag inserted to avoid data-loss |
SQLInstance |
SQL Server instance |
host |
Hostname of server hosting SQL Server instance |
query_hash |
queryhash in decimal format |
query_hash_hex |
queryhash in hexadecimal format |
query_plan_hash |
queryplan_hash in decimal format |
query_plan_hash_hex |
queryplan_hash in hexadecimal format |
SqlHostName |
Host that produced the query |
AxUser |
AX user_id |
SqlUser |
SQL user_id: it is a domain user |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
cpu_time |
Integer, microseconds of cpu time |
duration |
Integer, microseconds of elapsed time |
logical_reads |
Integer, number of pages read from buffer |
physical_reads |
Integer, number of pages read from storage |
row_count |
Integer, number of rows affected |
writes, number of pages written |
Integer, number of pages written |
session_id |
String, SQL session_id (spid) |
cursor_id |
String, SQL cursor_id |
AxSession |
String, AX session_id |
sqlXeFetches metric is exposed in a chart for a first glance and in a table for a deeper insight overview.
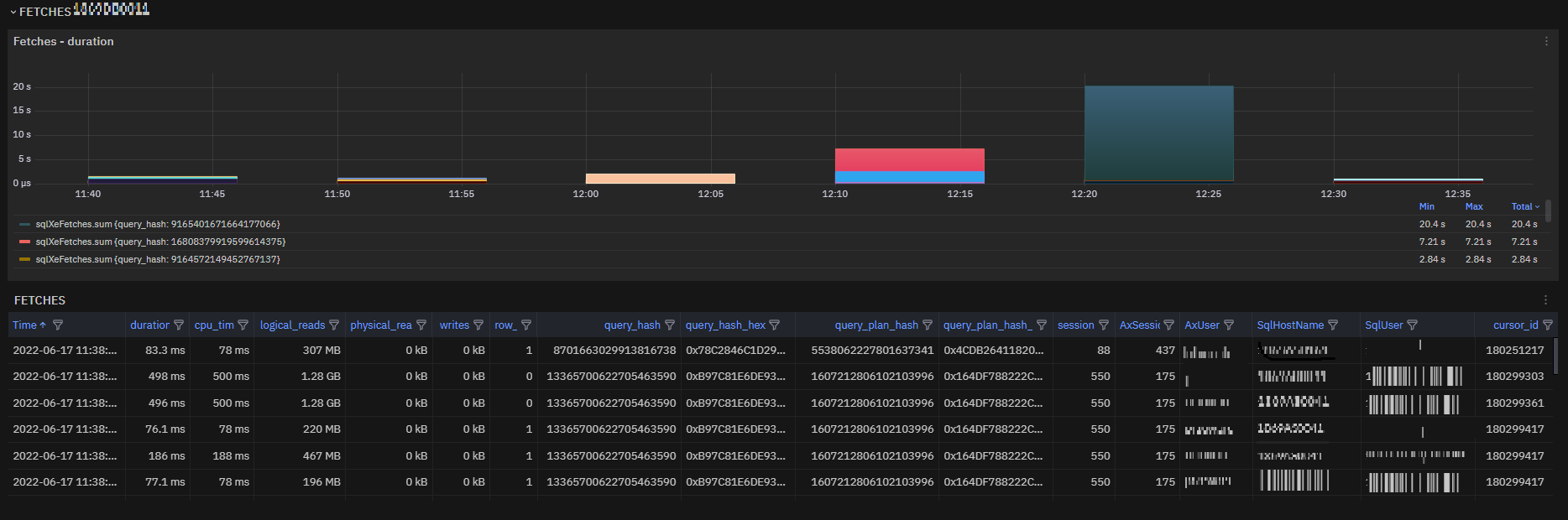
Fig. 185 sqlXeFetches table and chart for duration group by query_hash¶
Monitoring of Microsoft SQL Server Blocking/Deadlocks¶
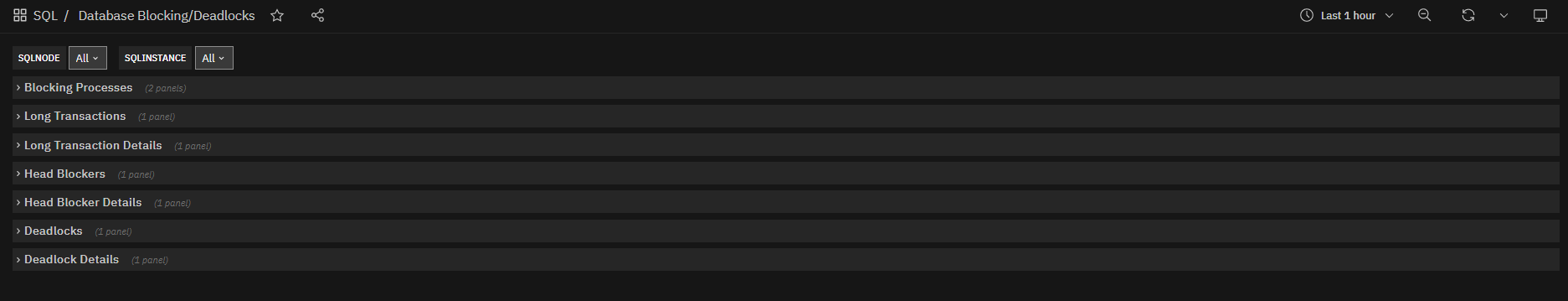
Fig. 186 Microsoft SQL Server Blocking/Deadlocks dashboard¶
Blocking/Deadlocks instances status¶
The first row of charts shows two Windows Performance Counters exposed my MS SQL Server:
General_Statistics::Processes_blocked
Locks::Number_of_Deadlocks_persec

Fig. 187 Blocked Processes and Deadlocks time series charts¶
Exposed metric: SQLLongTransaction¶
SQLLongTransaction metric collects details about all transactions lasting longer than 15 seconds.
This metric is based on Extended events combined with queries on DMVs.
SQLLongTransaction,host=axprodsqlnode,AXUser=axuser1,LoginName=dm\aossvcuser,ClientHostName=axpraos01,SQLInstance=axprodsqlnode NrSessions=1i,ALLSQLSessions="171",ALLAxSessions="893",MaxAxSession="893",ALLDurations="30",MaxDuration=30i,ALLCurrentRequest="32",ALLLastBatches="32",MaxLastBatch=32i
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
host |
Hostname of server hosting SQL Server instance |
AxUser |
AX user_id |
LoginName |
SQL user_id: it is a domain user |
ClientHostName |
Host that produced the query |
SQLInstance |
SQL Server instance |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
NrSessions |
Integer, numeber of sessions |
ALLSQLSessions |
String, list of SQL session_id (spid) |
ALLAxSessions |
String, list of AX session_id |
MaxAxSession |
String, AX session_id corresponding to maximum transaction duration |
ALLDurations |
String, all transaction durations in seconds |
MaxDuration |
Integer, maximum transaction duration in seconds |
ALLCurrentRequest |
String, all current requests elapsed time since request’s start in seconds |
ALLLastBatches |
String, all last batch duration in seconds |
MaxLastBatch |
Integer, maximum batch duration in seconds |
SQLLongTransaction metric metric is exposed in a chart to show an overview.
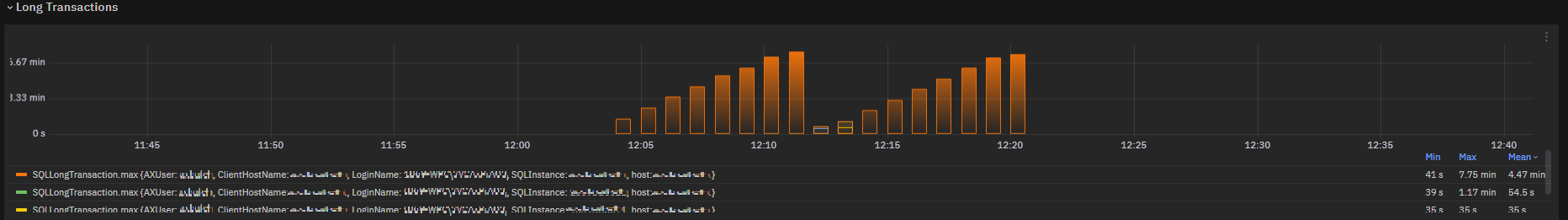
Fig. 188 Long transactions chart: MaxDuration field¶
SQLLongTransaction metric is also exposed in a table for deeper insights.
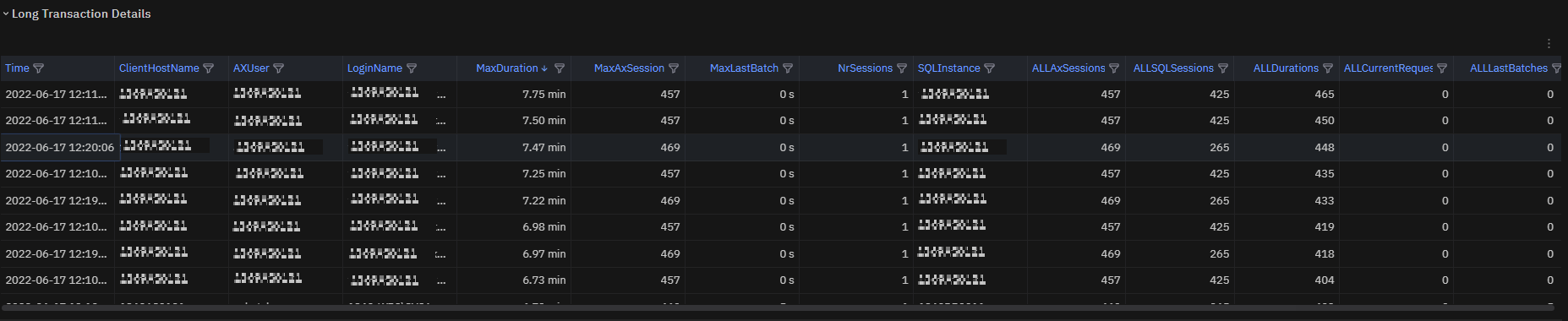
Fig. 189 Long transactions table¶
Exposed metric: SQLHeadBlockers¶
SQLHeadBlockers metric collects details about all blocking and blocked transactions.
This metric is based on Extended events combined with queries on DMVs.
SQLHeadBlockers,host=axprodsqlnode,AXUser=axuser1,LoginName=dm\aossvcuser,ClientHostName=axpraos01,SQLInstance=axprodsqlnode AXSession="893",SQLSession="171",MaxWaitInSec=23i,NrOfWaitingSessions=1i,BlockedAxUsersChain="axuser1>>axuser2",BlockedAxSessionsChain="893>>27",BlockedSQLSessionsChain="171>>334",BlockedSQLClientHostName="axpraos01>>axpraos01",AllWaitsinSecList="0>>23"
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
host |
Hostname of server hosting SQL Server instance |
AxUser |
AX user_id |
LoginName |
SQL user_id: it is a domain user |
ClientHostName |
Host that produced the query |
SQLInstance |
SQL server instance |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
AXSession |
String, AX session_id of head blocker |
SQLSession |
String, SQL session_id (spid) of head blocker |
MaxWaitInSec |
Integer, maximum waiting time of blocked sessions |
NrOfWaitingSessions |
Integer, number of blocked sessions |
BlockedAxUsersChain |
String, schema of blocked chain for AX users |
BlockedAxSessionsChain |
String, schema of blocked chain for AX sessions |
BlockedSQLSessionsChain |
String, schema of blocked chain for SQL sessions |
BlockedSQLClientHostName |
String, schema of blocked chain for SQL host clients |
AllWaitsinSecList |
String, schema of blocked chain with waiting time detail in seconds |
Blocked chain notation:¶
Symbol |
Description |
|---|---|
>> |
Used to indicate a block, on the left the blocking session/user and on the right the blocked sessions/users. Example: axuser1 >> axuser2 |
| |
Used to separate sessions/users at the same block level of the chain. Example axuser1 >> (axuser4|axuser3|axbatchuser2) |
() |
Used to group sessions/users at the same block level of the chain. Example axuser1 >> (axuser2|axuser3) |
SQLHeadBlockers metric metric is exposed in a chart to show an overview.
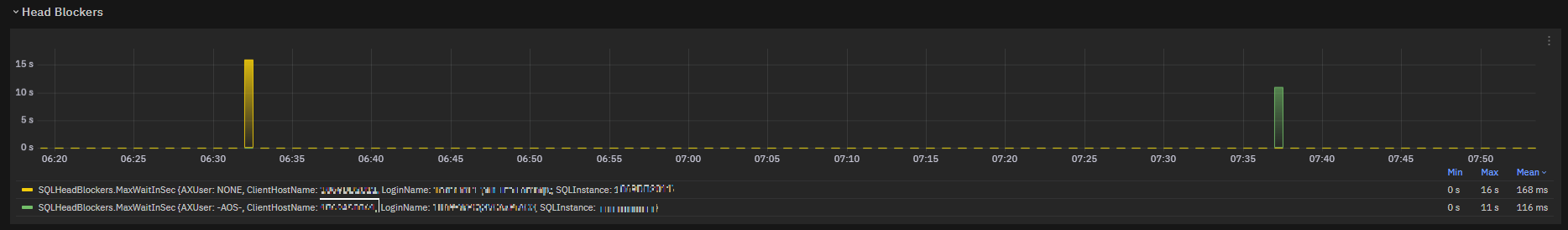
Fig. 190 Head Blockers chart: MaxWaitInSec field¶
SQLHeadBlockers metric is also exposed in a table for deeper insights.
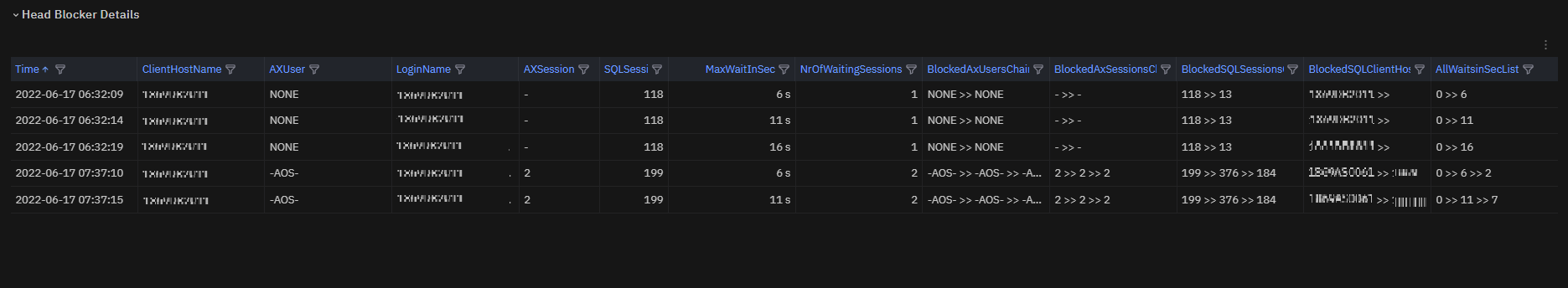
Fig. 191 Head Blockers table¶
Exposed metric: SQLDeadlockStats¶
SQLDeadlockStats metric collects details about all blocking and blocked transactions.
It is based on Extended events combined with queries on DMVs.
SQLDeadlockStats,host=axprodsqlnode,LoginName=dm\aossvcuser,ClientHostName=axpraos01,SQLInstance=axprodsqlnode,WaitObjectname=AXPRODDB.dbo.TMSRATEDETAILS,WaitIndexname=I_102463RECID
NrOfVictims=1i,SQLSessionId="188",Waittime=435i,WaitResource=""KEY: 5:72057763523526656 (62c716f85be8)",WaitMode="X",WaitObject="AXPRODDB.dbo.TMSRATEDETAILS",WaitIndex="I_102463RECID",WaitStatement="(@P1 int,@P2 bigint)DELETE FROM TMSRATEDETAILS WHERE (((PARTITION=5637144576) AND (DATAAREAID=N'001')) AND ((REFTABLEID=@P1) AND (REFRECID=@P2)))",SqlDeadlockHash="deadlock_16FAB3731CED4000_20220621_193840"
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
host |
Hostname of server hosting SQL server instance |
LoginName |
SQL user_id: it is a domain user |
ClientHostName |
Host that produced the query |
SQLInstance |
SQL server instance |
WaitObjectname |
Name of waited object |
WaitIndexname |
Name of waited index |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
NrOfVictims |
Integer, number of deadlock’s victims |
SQLSessionId |
String, |
Waittime |
Integer, time waited by victim process in seconds |
WaitResource |
String, waitresource for victim process |
WaitMode |
String, waitmode for victim process |
WaitObject |
String, name of wait object for victim process |
WaitIndex |
String, name of wait index for victim process |
WaitStatement |
String, victim process statement |
SqlDeadlockHash |
String, filename to retrieve the xml_deadlock_file |
SQLDeadlockStats metric is exposed in a chart to show an overview.
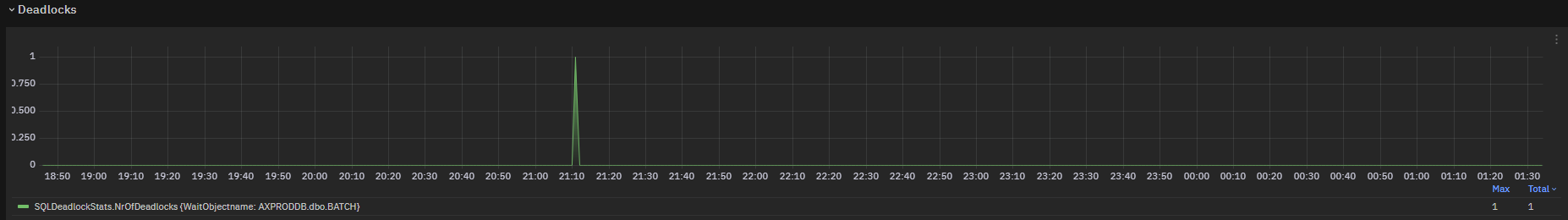
Fig. 192 Deadlocks chart: NrOfVictims field¶
SQLDeadlockStats metric is also exposed in a table for deeper insights.

Fig. 193 Deadlocks table¶
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 & Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations Batch Jobs¶
This part is valid both for
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations
the only differences are in tag values.
The main objective is to have visibility on the internal AX batch job scheduling mechanism, in particular it is useful to see when the system is unable to dispose of pending batch jobs.
The results visible in these metrics must then be linked with the other metrics collected if the causes are to be analyzed.
Link on main dashboard¶
The main dashboard displays the Total Overdue Batch Tasks chart with the count per minute of the batch jobs in overdue, highlighting the Group ID. The link top on the left of the chart gives us access to details on batch job sessions.

Fig. 194 AXBatchOverdueByGrp chart for cntBatchOverdue field¶
Batch job sessions¶
Exposed metric: AXBatchOverdueByGrp¶
The first chart is the same of main dashboard, with the added filter on database name.
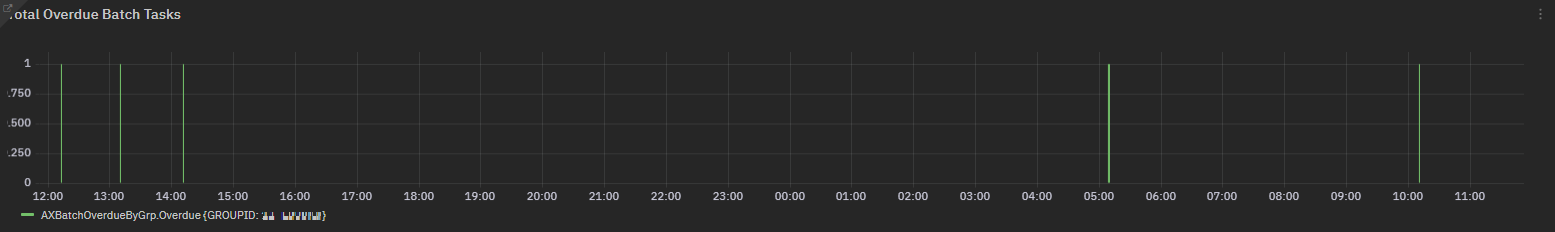
Fig. 195 AXBatchOverdueByGrp chart for cntBatchOverdue field¶
AXBatchOverdueByGrp metric collects details on overdue batches
AXBatchOverdueByGrp,uniquifier=0,GROUPID=WPAXT_G_11,DBName=DEV6AX,DBServername=AXDBHOST,DBServicename=MSSQLSERVER,SQLInstance=AXDBHOST TotalOverdueMinutes=1i,cntBatchOverdue=1i
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
uniquifier |
Technical tag to avoid duplicates |
GROUPID |
AX batch job group |
DBName |
Database name |
DBServername |
MSSQL server host name |
DBServicename |
MSSQL server service name |
SQLInstance |
MSSQL server instance name |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
TotalOverdueMinutes |
Integer, sum over overdue time |
cntBatchOverdue |
Integer, number of overdue batches |
Exposed metric: AXBatchSessionOverviewByAOS¶
AXBatchSessionOverviewByAOS metric collects details on batch sessions status
AXBatchSessionOverviewByAOS,uniquifier=0,SERVERID=01@AXAOS01,host=AXDBHOST,AOSServer=AXAOS01,AOSInstance=01,DBName=DEV6AX,DBServername=AXDBHOST,DBServicename=MSSQLSERVER,SQLInstance=AXDBHOST maxBatchSessions=16i,freeBatchSessions=5i,runningBatchSessions=11i
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
uniquifier |
Technical tag to avoid duplicates |
SERVERID |
AOS Service instance name |
AOSServer |
Hostname of batch AOS Service |
AOSInstance |
Instance ID of batch AOS Service |
DBName |
Database name |
DBServername |
MSSQL server host name |
DBServicename |
MSSQL server service name |
SQLInstance |
MSSQL server instance name |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
maxBatchSessions |
Integer, maximum number of active batch sessions |
freeBatchSessions |
Integer, number of free batch sessions |
runningBatchSessions |
Integer, number of executing batch sessions |
Chart visualizing all running batch sessions per each AOS Server.
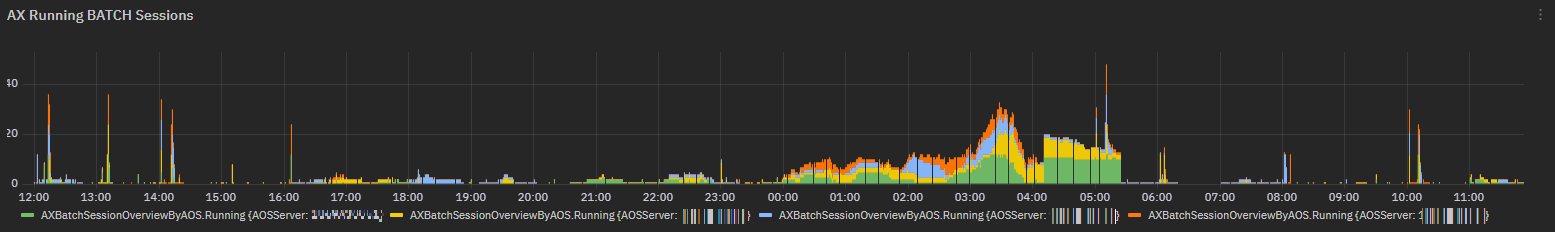
Fig. 196 AXBatchSessionOverviewByAOS chart for runningBatchSessions field¶
Chart visualizing all free batch sessions per each AOS Server.
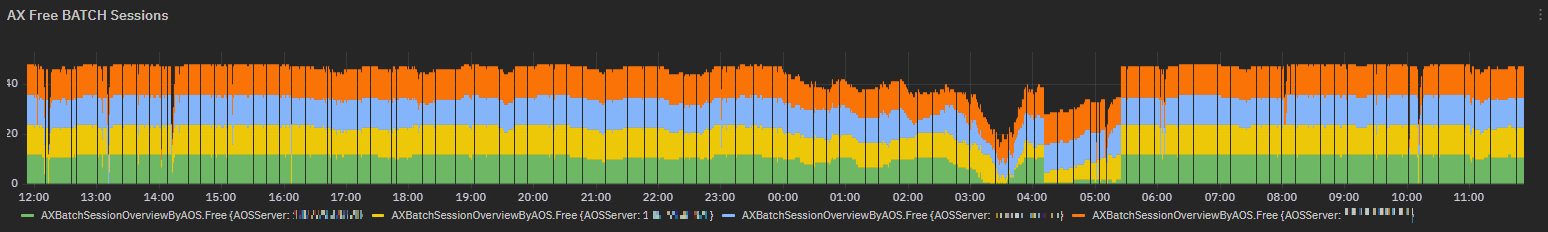
Fig. 197 AXBatchSessionOverviewByAOS chart for freeBatchSessions field¶
Batch AOS Server status¶
To facilitate the link between the batch execution flow and the server status, we summarize two Windows Performance Counters here:
Batch job sessions¶
Exposed metric: AXBatchOverdue¶
AXBatchOverdue metric collects details on overdue batch tasks
AXBatchOverdue,uniquifier=0,DBName=DEV6AX,DBServername=AXDBHOST,DBServicename=MSSQLSERVER,SQLInstance=AXDBHOST BOverdueMinutes=10i,GROUPID=\"WPAXT_G_11\",Batchjobid=\"5641145287\",Batchid=\"5655004328\",BCaption=\"Batch task test 1\",BJCaption=\"Batch job test\",Classnumber=\"1013860\"
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
uniquifier |
Technical tag to avoid duplicates |
DBName |
Database name |
DBServername |
MSSQL server host name |
DBServicename |
MSSQL server service name |
SQLInstance |
MSSQL server instance name |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
BOverdueMinutes |
Integer |
GROUPID |
String, batch group ID |
Batchjobid |
String,batch job recid |
Batchid |
String, batch task recid |
BCaption |
String, batch task caption |
BJCaption |
String, batch job caption |
Classnumber |
String, batch task class number |
Same metric is exposed in a chart to show an overview.
Fig. 200 AXBatchOverdue chart for BOverdueMinutes field¶
and also in a table for deeper insights.

Fig. 201 AXBatchOverdue table¶
Configuration on NetEye¶
The SQLTrace module extends the ITOA module and shares the structure with it for users, data sources and dashboards.
Variable Name |
Description |
|---|---|
<DATABASE> |
InfluxDB database where data must be written |
<XERETENTIONPOLICY> |
InfluxDB retention policy used for sqlXeEvents and sqlXeFetches metrics |
InfluxDB Retention Policies for SQLTrace¶
This paragraph integrates the relative section for the Telegraf agent.
The sqlXeEvents and sqlXeFetches metrics have high cardinality , this problem is limited by choosing an appropriate retention_policy with appropriate duration: our advice is to create a 2-week retention policy.
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "<XERETENTIONPOLICY>" ON "<DATABASE>" DURATION 2w REPLICATION 1 shard duration 6h
Write Data to InfluxDB¶
This paragraph integrates the relative section for the Telegraf agent configuration.
Let’s create two copies of the [[outputs.influxdb]] section, the first one will write data into default retention policy and the second one into the new <XERETENTIONPOLICY> retention policy.
The first section configures how Telegraf writes to the default InfluxDB retention policy, then we add the namedrop option to prevent sqlXeEvents and sqlXeFetches metrics to be written in default retention policy:
[[outputs.influxdb]]
namedrop = ["sqlXeEvents","sqlXeFetches"]
urls = ["https://influxdb.neteyelocal:8086"]
The second section defines how Telegraf writes to the <XERETENTIONPOLICY> retention policy, then we add the namepass option to force sqlXeEvents and sqlXeFetches metrics to be written in this retention policy:
[[outputs.influxdb]]
namepass = ["sqlXeEvents","sqlXeFetches"]
urls = ["https://influxdb.neteyelocal:8086"]
retention_policy = "<XERETENTIONPOLICY>"
Configuration of SQLTrace¶
Windows Administrator installing the service must provide a configuration file in toml format syntax. The name of configuration file must be sqltrace.conf.
The SQLTrace agent sends its metrics to NetEye exactly like a Telegraf agent installed on a Windows server, which means that in section [output.nats] are used same address, subject and tls certificates are the same used in *[[outputs.nats]]* section of Telegraf configuration file.
Variable Name |
Description |
|---|---|
<MSSQLINSTANCENAME> |
MSSQL instance we want to monitor, example: PBZMSSQL063\SQLTEST |
<XEVT_SQL_DURATION> |
SQL Extended Event Session Name to be used for SQL Query durations analysis, example: WPPERF_SQL_DURATION |
<XEVT_SQL_CURSORS> |
SQL Extended Event Session Name to be used for SQL Query durations analysis, example: WPPERF_SQL_CURSORS |
<XEVT_BLOCKING_DATA> |
SQL Extended Event Session Name to be used for SQL Query durations analysis, example: WPPERF_BLOCKING_DATA |
<QUERIESPATH> |
Path where query files are sored, example: C:\MSSQLTrace\PBZMSSQL063\queries |
<PLANSPATH> |
Path where query files are sored, example: C:\MSSQLTrace\PBZMSSQL063\plans |
<DEADLOCKSPATH> |
Path where query files are sored, example: C:\MSSQLTrace\PBZMSSQL063\deadlocks |
<DATABASENAME> |
Database name for extention monitoring modules |
<NATSADDRESS> |
NATS io endpoint, example nats://neteye-sat1.lan.local:4222 |
<NATSSUBJECT> |
NATS subject to identify the publisher/producer of data, on neteye it is the same used for Telegraf agent: telegraf.metrics |
<CA_PATH> |
Path to valid CA, example C:/SQLTrace/certs/neteye-sat1-root-ca.crt |
<CERT_PATH> |
Path to certificate, example C:/SQLTrace/certs/telegrafmetrics-neteye-sat1.crt.pem |
<PRIVATEKEY_PATH> |
Path to private key, example C:/SQLTrace/certs/private/telegrafmetrics-neteye-sat1.key.pem |
## SQL extended Events Channel Configuration
[main]
#Name of SQL Server instance to monitor and collect advanced performance data
#Required: YES
#
dataSource="<MSSQLINSTANCENAME>" #(mandatory) sql instance name, remember backslash must be escaped \\
## Define SQL Extended Event Session names for advanced performance analysis.
# this names are used in the Prepair4SQLDMVMonitor.ps1 to created the Sessions. You can choose the names for this SQL XE Sessions as you like.
# The names must be unique on the SQL Server Instance.
# The SQL Agent need this names to collect, analyse and send this performance data.
#
# SQL Extended Event Session Name to be used for SQL Query durations analysis
# Required: no
# Default value is empty. => query performance data are not collected
queriesProbe="<XEVT_SQL_DURATION>"
# SQL Extended Event Session Name to be used for SQL cursor fetch durations analysis
# Required: no
# Default value is empty. => cursor fetch performance data are not collected
#
fetchesProbe="<XEVT_SQL_CURSORS>"
#SQL Extended Event Session Name to be used for SQL Blocking and Deadlock analysis.
#Required: no
# Default value is empty. => blocking and deadlocking data are not collected
#
blockingsProbe="<XEVT_BLOCKING_DATA>"
## SQL Queries and SQL Queryplan are stored on local disk. Please calculate approx 15-20 GB of Storage space for this file locations
## The Account running the SQLDMVMonitor must have read write permissions on that local file path
[storage.fileSystem]
# Path where queries are stored (backslash must be escaped \\)
# Required: YES
#
queriespath = "<QUERIESPATH>"
# Path where queryplans are stored (backslash must be escaped \\)
# Required: YES
#
planspath = "<PLANSPATH>"
# Path where deadlocks are stored (backslash must be escaped \\)
# Required: NO, if not present queriespath is used
#
#deadlockspath = "<DEADLOCKSPATH>"
## compress query plan files as zip in the directory to save space, default true
# zipped = true
## queryplan and query files retention in days (if lower than 1 it is set to 1, default 15)
## days the files will be taken in the queriespath and planspath. It check the modified time of files
# retentionInterval = 15
## interval for touching the plan and query files. Touch will be refresh the modifiedtime attribute of the file.
## if lower than 1, set to 1, default 30 minutes
# updateInterval = 30
## interval for check of files actually present in filesystem (if neteyeremotestorage is active remote check is also triggered)
## if lower than 1, set to 1, default 24 hours
# checkIntervalHours = 24
## Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012: related options
# Required: No
#
# [dmv.DX.AX2012]
# Name of AX Business DB located on the datasource. This is used to calculate AX 2012 Batch Job and Task overdue
# default value : empty (no AX Business DB)
# Required: No
# databaseName = "<DATABASENAME>" #AX2012 database name
## SQL server related options
# Required: No
#
# [dmv.DX.MSSQL]
# Database name for advanced monitoring (e.g. Database growth of tables and indexes)
# default value ="master"
# Required: NO
# databaseName = "<DATABASENAME>"
## Send Measurements to NATS
[output.nats]
# URL(address) of NATS Server
# Requried:YES
#
address = "<NATSADDRESS>" #(mandatory) nats-server endpoint
## NATS subject to identify the publisher/producer of data
# Requried:YES
#
subject = "<NATSSUBJECT>" #(mandatory) nats-server subject
## NATS TLS Config
# set to true TLS is used.
# DEFAULT value is false
#
# secure = true
secure = true #set as true if TLS is needed, if omitted default value is false
# TLS Config Parameters are required if parameter secure is set to true
# tls_ca = "<CA_PATH>" #CA_PATH
# tls_cert = "<CERT_PATH>" #certificate path
# tls_key = "<PRIVATEKEY_PATH>" #private key path
#defines the nats channel to send keepalive & monitoring data infos to NetEye server, disabled by default
#[output.tornado]
#topic = "tornado_nats_json.<topic>" #mandatory, it represents the subject on nats-server (configured in tornado_nats_json_collector topics on NetEye)
#keepaliveInterval = 5 #interval in seconds for keepalive message, if omitted default value is 5 seconds;
#monitordataInterval = 30 #interval in seconds for monitordata message, if omitted default value is 30 seconds;
#hostnameformat="fullqualified" #default is "fullqualified", otherwise put "hostonly"
#tornado_dedicated_connection: all the following settings must be used to open a dedicated connection for tornado messages (in case destination addresses and/or certifcate are different)
#address = "TORNADO-NATS-ADDRESS" #optional (see tornado_dedicated_connection above)
#secure = true #optional (see tornado_dedicated_connection above) set as true if TLS is needed, if omitted default value is false
#tls_cert = "<PATHVALUE>\\<filename>.crt.pem" #optional (see tornado_dedicated_connection above) certificate path
#tls_key = "<PATHVALUE>\\<filename>.key.pem" #optional (see tornado_dedicated_connection above) private key path
#base settings (embedded in agent)
#[output.nats.retention_policy_tag]
#active=true #if false, this feature is disabled: no retention tag is sent
#default="autogen" # default tag value for all measurements that are not exlicitly defined in (retention_policy_tag.<> measurements) defining the retention on influx
#tag_name="retention_policy" # tag name on the measurments which define the retention
#[output.nats.retention_policy_tag.queryhashcodemetrics] # retention_policy_tag.<retentionvalue> # <retentionvalue> is retention tag value for measurements in "measurements" array following
#measurements = ["sqlXeEvents","sqlXeFetches"] # measurment names to which retention policy example tag queryhashcodemetrics is added
#
[output.neteyeremotestorage]# this part is request to upload sql files on neteye-saas (where mssql-fileserver is installed and configured)
outChannel = "sqltrace.out.perfmon-dev.wp.lan" #mandatory, nats publish channel, for files upload, it is not allowed to use the same value as inChannel
inChannel = "sqltrace.in.perfmon-dev.wp.lan" #mandatory, nats subscription channel, used to receive feedbacks from server (file upload completed ...), it is not allowed to use the same value as outChannel
#connectioncheckIntervalSeconds = 15 #optional, seconds interval for ping test (default is 15 seconds)
#neteyeremotestorage_dedicated_connection: all the following settings must be used to open a dedicated connection for neteyeremotestorage messages (in case destination addresses and/or certifcate are different)
#address = "NETEYEREMOTESTORAGE-NATS-ADDRESS" #optional (see neteyeremotestorage_dedicated_connection above)
#secure = true #optional (see neteyeremotestorage_dedicated_connection above) set as true if TLS is needed, if omitted default value is false
#tls_cert = "<PATHVALUE>\\<filename>.crt.pem" #optional (see neteyeremotestorage_dedicated_connection above) certificate path
#tls_key = "<PATHVALUE>\\<filename>.key.pem" #optional (see neteyeremotestorage_dedicated_connection above) private key path
Installation¶
The Installation process is divided in three phases:
Define the configuration file
sqltrace.confSetup the SQL Server Instance with the required permissions and configurations
Install the SQL DMV Monitor Service
Configuration file location¶
The setup will register the location of the config file in the startup parameters of the service. The file will not be copied: for this it is important that a secure location is used for this config file.
The service reads the config file at each start. The config file can be located also on a local path or on a shared path.
Please take into consideration that the user that is installing the SQL DMV Monitor Service and the SQLTrace Service Account under which the SQL DMV Monitor Service is running must have read access to this file.
Note
SQLTrace Service Account: Windows account under which the SQL DMV Monitor Service can run. The account must be a Windows account or a valid gMSA.
Setup of SQL Server Instance¶
Prerequirements¶
PowerShell script requires Microsoft System CLR Types for Microsoft® SQL Server® 2012 and Microsoft SQL Server® 2012 Shared Management Objects installed on the computer where you run the script. The SMO must be at least for verions SQL 2012.
User executing the PowerShell script must have SysAdmin rights on the SQL Server Instance
A valid configuration file
sqltrace.confSQLTrace Service Account under which the SQL DMV Monitor Service will run
SQLExtEventDirpath where the SQL Server Service should write the SQL Extended Event files
Note
SQLExtEventDir is checked at each start from SQL Server Service.
PowerShell script¶
Run the script Prepair4SQLDMVMonitor.ps1 provided together with msi file.
The script will validate and set the needed configurations and permissions for the SQL Server Instance which you want to monitor. As Result the script returns a result which describes if the SQL Server Instance is prepared successfully.
A detailed description regarding the script parameters can be found in the PowerShell script.
Examples:
Validate if permissions and configurations are set without applying them: useful to check and validate configuration. SQLExtEventDir path to C:tmp, username for SQLTrace wp\test. Expected result for $result.SQLInstancePrepared is True.
$result=.\Prepair4SQLDMVMonitor.ps1 -SQLTraceConfigFile C:\tmp\sqltrace.conf -SQLExtEventDir C:\tmp -SQLTraceServiceaccount 'wp\test' -OnlyValidate $result.SQLInstancePrepared
Apply permissions and configurations, SQLExtEventDir path to C:tmp, username for SQLTrace wp\test. Expected result is True.
$result=.\Prepair4SQLDMVMonitor.ps1 -SQLTraceConfigFile C:\tmp\sqltrace.conf -SQLExtEventDir C:\tmp -SQLTraceServiceaccount 'wp\test' $result.SQLInstancePrepared
Installation Prerequisites¶
User running installation must have Windows local administration rights.
Name |
|---|
Windows Operation System: Windows 2012 R2 or higher (64 Bit) |
Name |
|---|
.NET Framework 4.5.2 or higher |
Installing the SQL DMV Monitor Service¶
Optionally a SQLTrace Admin Account can be defined: this allows users other than the Windows Administrator to have the permissions to restart the service. For example it is useful for the purpose of managing the service remotely via PowerShell.
UI installation¶
Start the installer and follow each step.
Silent mode installation¶
Run msiexec from command line, here you can see a detailed description regarding msiexec parameters.
To run the installation in silent mode use following syntax:
msiexec /i "SQLDMVMonitor-x64.msi" /qn /L*V <logfile> <SQL DMV Setup Parameters>
Setup Parameters¶
Variable Name |
Description |
|---|---|
INSTALLFOLDER |
Path where the binaries will be installed. Default <ProgramFiles>SQLDMVTracing |
LICENSEACCEPTED |
Mandatory - Value must be set to “1” to confirm and accept License agreement. Default is “0” |
SQLDMVTRCCONFDIR |
Path where the <SQLDMVCONFIG> file must exist. This parameter is REQUIRED. The setup will register the location of the config file in the startup parameters of the service (see service.msc - SQLDMVMonitor). The file will not be copied. For this it is important that a secure location is used for this config file. The service read the config file each time it is started. The config file can be located also on a local path or on a shared path. Please take into consideration that the user that is installing the SQL DMV Tracing Service and the Account under which the SQL DMV Service is running must have read access to this file. Setup will check that in this directory or subdirectory a valid config file with then name sqltrace.conf exist. The Setup check that a config file exist in 3 directories using this sequence:
|
SQLDMVTRCSERVICEACCOUNT |
Windows Account whith which the SQL DMV Tracing service will run. e.g. <domain\accountname> . Please take into consideration that the PowerShell preparescript has set the needed permissions for this user. |
SQLDMVTRCSERVICEACCOUNTPWD |
Passsword of the Windows Account. set Password “” if you use a gMSA |
SQLDMVTRCASSIGNADMIN |
If set to 1 a Windows Account/Group defined with param SQLDMVTRCADMINACCOUNT becomes the permissions to stop/start/query the SQL DMV Tracing Service.Default is 0 (false) |
SQLDMVTRCADMINACCOUNT |
Windows Account/Group which will have the permissions to start/stop the SQL DMV service. Setup will assign the appropriate permissions. Specify <Domainaccountname> or <Domaingroup>. Mandatory if SQLDMVTRCADMINACCOUNT=1 |
MSINEWINSTANCE |
If set to 1 you can install until 5 additional sqldmvmonitor Agents |
TRANSFORMS |
String Value define which sqldmvmonitor Agent Instance can be installed allowed values are: “:I01”,”:I02”,”:I03”,”:I04”,”:I05” |
Examples of installation¶
SQLTrace Service Account is set to wp\sqlsvctrc. SQLTrace Admin Account is not set. Install dir is default one. SQL DMV Monitor config file is located in C:tmp:
msiexec /i "SQLDMVMonitor-<version>-x64.msi" /qn /L*V c:\tmp\install.log SQLDMVTRCCONFDIR="c:\tmp" LICENSEACCEPTED="1" SQLDMVTRCSERVICEACCOUNT="wp\sqlsvctrc" SQLDMVTRCSERVICEACCOUNTPWD="password" SQLDMVTRCASSIGNADMIN=0
SQLTrace Service Account is set to wp\sqlsvctrc. SQLTrace Admin Account is set to wp\SQLDMVadmingrp . Install dir is default. SQL DMV config file is located in C:tmp:
msiexec /i "SQLDMVMonitor-<version>-x64.msi" /qn /L*V c:\tmp\install.log SQLDMVTRCCONFDIR="c:\tmp" LICENSEACCEPTED="1" SQLDMVTRCSERVICEACCOUNT="wp\sqlsvctrc" SQLDMVTRCSERVICEACCOUNTPWD="password" SQLDMVTRCASSIGNADMIN=1 SQLDMVTRCADMINACCOUNT="wp\SQLDMVadmingrp"
Install SQL DMV Monitor with specific Instance 01 installing not in quite mode:
msiexec /i sqldmvmonitor-<version>-x64.msi /L*V c:\tmp\install-I01.log MSINEWINSTANCE=1 TRANSFORMS=":I01"
Return codes msiexec¶
In silent mode you can verify if installation was successful by checking the exitcode of msiexec.
If exit code is 0 installation was successful. For details of error codes refer to error Error codes.
Setup Error and Failures¶
Setup will fail if:
Config file is not found/readable
Content of config file is not valid:
Missing or wrong NATS server
Missing or wrong NATS port
Details of error can be found in the msi log file or in the application eventlog.
Error |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Invalid command line argument. Consult the Windows Installer SDK for detailed command line help. |
This happens if you run the msi using the parameter for Multiinstance e.g. MSINEWINSTANCE=1 TRANSFORMS=”:I01”
The error occures if the Instance is already installed. In the msi log File you will find following error.
Extract from log: “Specified instance {XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX} via transform is already installed. MSINEWINSTANCE requires a new instance that is not installed. MainEngineThread is returning 1639”
|
Remote Storage Test |
It is possibile to test the connection to remote NetEye file storage using the option –test-remotestorage: "C:\Program Files\SQLDMVMonitor\I00\DMVmonitor.exe" -config ".\sqltrace.conf" -instanceId I00 --test-remotestorage
|
Tornado Test |
It is possible to send Tornado test messages using the option –test-tornado: "C:\Program Files\SQLDMVMonitor\I00\DMVmonitor.exe" -config ".\sqltrace.conf" -instanceId I00 --test-tornado
|
Uninstall instances of SQL DMV Monitor Service¶
From Control Panel¶
Find SQLDMVMonitor in installed programs list then right mouse click and choose option Uninstall.
In silent mode¶
Using the product code (see list of Product Codes).
msiexec /x "{XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX}" /qn /L*V c:\tmp\uninstall.log
Upgrade from a Previous Version¶
Each upgrade will be handled as Major Upgrade. During Upgrade Windows Installer will uninstall previous version before running the installation.
Windows Installer checks the current installed version using the Product Code Guid of the msi bundle: this is important when you deploy the agent using e.g. Powershell DSC.
The ProductCode for the actual version can be found in this document under table List of ProductCode for released versions.
Please take in consideration that you have to run the upgrade/installation with the necessary setup parameters (like first installation). If during installation of the new version an error occurs, the old version will not be restored!
Note
upgrading from version 0.1.x during uninstall service is stopped but process is still running for approx 30 sec. To solve stop the service manually and check that process DMVMonitor is removed, then run the msi bundle.
Migrating to Version 0.4.x¶
When upgrading to Version 0.4.x from previous versions xevent session on MSSQL instance must be reconfigured for compatibility reasons: run the powershell script Prepair4SQLDMVMonitor.ps1 (as described in Instance setup).
This is needed to get all the required information about query fetches. The correct steps to migrate to the new version is:
Stop SQL DMV Monitor Service (DMVmonitor)
Run Prepair4SQLDMVMonitor.ps1 with the needed parameters (same parameters as during first setup)
Upgrade to new version running msi bundle of version 0.4.x (SQLDMVMonitor-v0.4.1-x64.msi)
Note
With the introduction of 0.4 the field types of Maxduration and MaxLastBatch in the measurment SQLLongTransaction has been changed from float to integer: this change could potentially cause an incompatibility issue on you time-series database. To solve the issue on InfluxDB, you have to drop the old measurment.
List of ProductCode for released versions¶
Version |
Productcodes for each instance |
|---|---|
0.6.3 |
Default={74A96618-F674-4014-8BEE-33DE94641FAF}
I01={09A594B7-C726-4240-88F1-8217B523E1C0}
I02={917F1862-E818-48D8-BF5E-D25075CFE20D}
I03={9BD4070D-1929-442C-B497-F052F53F841B}
I04={9D73E337-0CCF-44F0-8532-32EC86959014}
I05={04800B00-5D59-4F32-A486-14E48B219042}
|
0.6.2 |
Default={C11199B6-A319-4656-BD1B-269B82082722}
I01=92412086-2F9E-4733-B540-5A74CC714383}
I02=C1B55E60-1F00-4E2B-8093-A873E428B044}
I03=EE7130A1-C6AA-4DE4-958D-7325B6B6D47F}
I04=93EE9F7E-EE4B-4A49-B98B-4F0391A00080}
I05=C3E5AA61-B332-4CA0-A9CB-B571B8B9E4FE}
|
0.6.1 |
Default={48CFD745-41BB-4512-9B86-0920BEDFA7E3}
I01={162DE559-D1FE-44FA-AA80-E19A981B2227}
I02={74E402EA-97DC-4D34-8D7B-AF4CD9420375}
I03={942BCAD3-4241-4BDB-8CF9-9090DF4AA8B2}
I04={654C0EAB-EFA5-4578-9CF3-0DE91375E8CB}
I05={828507F3-6F4D-4D64-8C33-2ECD606FC6DF}
|
0.5.1 |
Default={CFFC1BC5-8CD6-4599-82C9-0AE5AC893794}
I01={C4D30AEA-767C-429C-A81A-1F2A8E17AAC6}
I02={73977971-69EB-4DDD-89F1-4013CCA81E1E}
I03={A6996681-A88D-4E14-8363-F425ECB6B87A}
I04={035D7D15-BDC3-4C2D-840A-BF6B5D89A631}
I05={A85323A3-1427-4558-8F7C-80F9460B18A1}
|
0.5.0 |
Default={09564825-3DCD-4DC2-96B7-B654710FE633}
I01={91237714-F050-4FF5-8822-898E84FD4EDF}
I02={1CD5C97B-B4F9-46CA-BAD6-19B51FF12639}
I03={AD0578DF-0E16-41A8-B46E-387474F913F1}
I04={564D433B-A35D-496C-8DA2-60DBBC1361AD}
I05={0BEB3595-41C3-4C25-8FF4-D1EB85336D1B}
|
0.4.1 |
Default={D02F7B07-52D9-4A38-BCAF-05A87E1F2EC7}
I01={DFE7859D-6BE4-4BC1-84C9-526D456690D1}
I02={4E9F6545-ADA6-40B6-9C70-8AAD9E4EFCBA}
I03={D3D5A5A1-9D98-4184-B14B-53F4E935BD5A}
I04={0AF49B0C-D026-4AEA-835C-1F60AD41EE31}
I05={F1C45643-0F46-4AB9-B1F4-A7B8ECFBCC34}
|
0.4.0 |
Default={AE113811-DAAD-47CB-ACB6-FAD8AC009663}
I01={5951BFAA-5AC0-4286-80E5-A4AF36C9C0F4}
I02={F9482AE2-59D5-4268-BFE5-FB520C43BD7B}
I03={C616CCCD-2C42-466F-A4FF-447AC21A283D}
I04={E8245FCC-57C0-4A99-9D7C-83C6FAF2C7B0}
I05={0EEC6F6A-7033-4B61-9865-267320542EBB}
|
0.3.1 |
Default={D0E7F4AF-82C4-4B58-87C9-89BDDBEE4779}
I01={45B4717D-9B42-4998-B98D-14729EB3290D}
I02={0E5CCFB0-9690-40A2-B216-548977CD54BC}
I03={E69C1A2F-5B5F-435D-8E6B-1E585A740BA8}
I04={E783C535-A7F1-4541-888B-FC0F8BCD5411}
I05={2FD332AC-4ED9-4A24-90EC-5CEB95006E4E}
|
0.3.0 |
Default={E05B5F69-C9DF-4C2C-8F0D-6A09030B83DB}
I01={C6C6D7B4-7C12-4558-82E8-432F3202CCF6}
I02={FDF69F06-8BBA-4B04-A775-4202DBC3DBA4}
I03={4C55C3F6-CA64-44B9-BC42-26E40CAE5544}
I04={A8384887-7F93-488D-81B1-BA76CA59FB61}
I05={74C3EBFF-DB81-46DE-B941-BD686CFEF718}
|
0.2.1 |
Default={001CA7CF-D87D-4108-A3B8-D271402FF92F}
I01={C6B860DE-634A-4146-9B64-A3AE6EC0A409}
I02={92FEB3FD-5CCB-4CDF-B531-8E5015E64008}
I03={5508CC78-DABF-49CC-B217-A3AD2E294B86}
I04={20D1C901-8DCB-4280-899D-AF05D33B0636}
I05={3D7D125F-51E3-414F-BE1B-19B9BEFA29F7}
|
0.2.0 |
Default={49689FD2-D834-4C3F-97FF-BC3BD7FEDAF0}
I01={7C41FC5C-7694-45C2-B937-8AD4AEF5F952}
I02={C1FF4CB6-26D4-4361-958F-4F8FC9BFCC0E}
I03={A6F06ACB-009E-47B8-A1AD-612946392825}
I04={9DB323F7-E431-465F-BD4D-42F570AE9837}
I05={3259D96B-3A1A-46F0-9D7F-A4A43EC44FE1}
|
0.1.1 |
Default={9A9628AC-47CC-4E08-B9A8-257FFC6A7EAC}
|