Iterating over Event fields¶
Sometimes a Tornado event might contain more than one event that needs to be processed by a filter or a rule. For this use case you can use the Iterator node to split one event into several to be processed.
The Tornado Iterator node relies on its field target to select the value to iterate over. That field must contain a valid accessor expression. If an event reaches the Iterator node, it will try to access a value from the Event, based on the given expression. If a value was found, Tornado will then try to iterate over the value, given it is an array or an object.
For each iteration, Tornado will add a field iterator to the event that contains the current iteration and the item of the iteration. The data of the event itself will not be modified during this operation, so the value that is being iterated over, will still be present.
The iteration here depends on the value type. If Tornado is iterating over an array, the iteration will be the zero-based position of the element in the array. If the value is a object, however, the iteration will be the key corresponding to the current value.
In case the extractor could not find the value, the value has the wrong type or the value is empty, no event will be passed to the iterator’s children.
Example¶
Let’s assume we have the iterator as defined below:
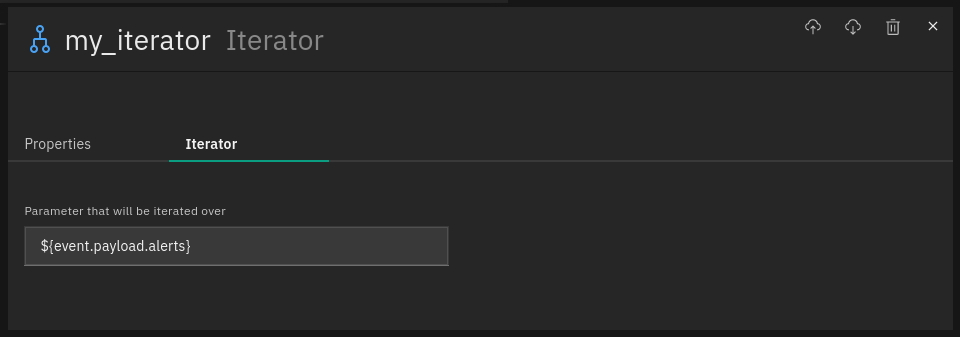
And the following event reaches the iterator:
{
"type":"my_webhook",
"created_ms":"17199237780000",
"payload":{
"host": "my_host",
"alerts": [
{
"service": "my_service1",
"state": "WARNING"
},
{
"service": "my_service2",
"state": "OK"
}
]
}
}
Then all child nodes of the iterator will receive the following two events:
{
"type":"snmptrapd",
"created_ms":"17199237780000",
"iterator": {
"iteration": 0,
"item": {
"service": "my_service1",
"state": "WARNING"
}
},
"payload":{
"host": "my_host",
"alerts": [
{
"service": "my_service1",
"state": "WARNING"
},
{
"service": "my_service2",
"state": "OK"
}
]
}
}
{
"type":"snmptrapd",
"created_ms":"17199237780000",
"iterator": {
"iteration": 1,
"item": {
"service": "my_service2",
"state": "OK"
}
},
"payload":{
"host": "my_host",
"alerts": [
{
"service": "my_service1",
"state": "WARNING"
},
{
"service": "my_service2",
"state": "OK"
}
]
}
}

